Success and failure of fanless PCs in industrial applications
No more failures when using fanless PCs
The operation of fanless PCs in industrial applications

The success of their use depends heavily on the requirements of the application and environment.
Shock and vibration resistance, protection class, ambient temperature, mounting options, required certificates.
Last updated: 9.12.2025
Fanless PCs are a successful solution for specific industrial, low-noise, or low-maintenance applications.
However, they are less suitable for performance-intensive desktop applications.
The success of their use depends heavily on the requirements of the application and environment.
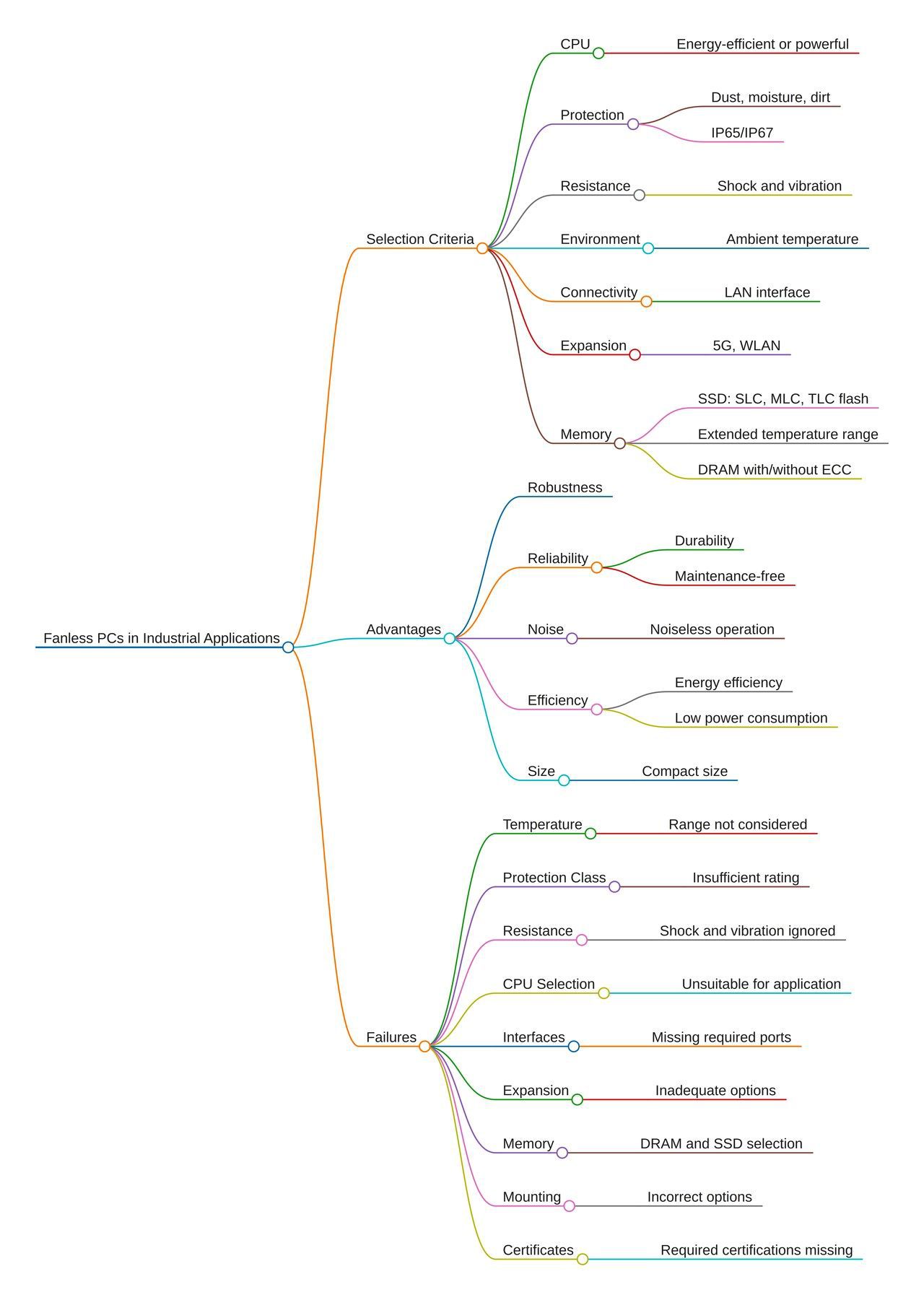
Important criteria for selecting fanless PCs:
• Energy-efficient or powerful CPUs
• Protection against dust, moisture, and dirt: IP65/IP67
• Shock and vibration resistance
• Ambient temperature
• LAN interface
• Extensions: 5G, WLAN
• Memory: SSD: SLC, MLC, or TLC flash, with or without extended temperature range DRAM with or without ECC
Advantages of fanless PCs:
Robustness: the devices offer protection against dust, moisture, and dirt. They can also be used in conditions with strong vibrations: their shock and vibration resistance is better than that of devices with fans. Failures due to dust ingress are extremely rare.
Reliability, durability, maintenance-free: fans are prone to failure. Wear and failure of fans due to dust, moisture, and vibrations are eliminated by the fanless design—this is essential for continuous operation in harsh environmental conditions. Higher MTBF values result in lower maintenance frequency and less downtime.
Fanless PCs are very well suited for remote and unattended installations.Noiseless: no fans are present and therefore no fan noise.
Energy efficiency and low power consumption: processors with low power consumption are used.
Thermal efficiency is supported by all components (GPU, SSD, chipsets) and heat dissipation is minimized – this ensures system stability. Under extreme load, the power output of the CPU is reduced. Power consumption s typically 10-35W for fanless PCs and 60 to over 200W for actively cooled PCs.Support for wide ranges of input voltages with high voltage tolerance.
Compact size: the devices can be installed in a space-saving manner. In control cabinets, machine controls, vehicles, kiosk terminals, via DIN rail mounting (top-hat rail mounting), VESA, rack, or desk mounting.
Failures occur when the selection criteria for the use of devices for your specific application and environmental conditions have not been taken into account.
These are:
• Temperature range: The device should be suitable for the extreme ambient temperatures that occur in your environment.
• Protection class: If exposed to water or dust, the device should have IP65/IP67 protection.
• Shock and vibration resistance requirements
• Selection of the most suitable CPU for your applications
• Required interfaces and expansion options
• Memory selection for DRAM and SSDs
• Mounting options
•Required certificates
Disadvantages of fanless PCs:
Performance limitations during intensive use due to overheating.
The use of CPUs with a low TDP means that processor performance is lower than that of more powerful CPUs with a higher TDP. Temperature control, which is normally achieved by means of a CPU fan controller, is the most critical factor here. Modern processors automatically reduce their clock frequency when critical chip temperatures are reached in order to generate less heat.High ambient temperatures: when used in control cabinets without air circulation, the service life of the electronics is reduced.
Limited cooling performance: Passive cooling is less effective than active cooling.
Unsuitable for powerful tasks such as CAD, simulations, or video editing due to lack of CPU/GPU performance or possible overheating and performance degradation.
Overheating and possible failure of components: CPU, SSDs, power supply.
Upgrading is limited by the thermal design
Areas of application:
• Edge computing, remote IoT, off-grid deployments
• Wind farms, solar parks, outdoor surveillance
• Remote controls, firewalls, VPN gateways, etc.
Applications
Automation: conveyor system, CNC machine control, test stations, robotics
Edge computing & IoT: energy grid monitoring, data analysis and machine learning (ML), predictive maintenance (PM) systems, sensor hubs
Transportation: Heavy-duty vehicles, buses, ships, railways
Remote IoT: Wind farms, solar parks, oil platforms
Medicine, emergency management in rescue operations
Visualization: Point of Sale, ATM, Kiosks, Vending Machines, Digital Signage
Military
Fanless Embedded PCs at 1ST-embedded
Now it's your turn: get informed and use the fanless PCs successful in your technological processes!
Consult your expert: Sven Trommer Tel. +4940-7003550
We look forward to hearing from you!
Jelena Dronowa, Head of Digital Media, Dipl.-Ing for Systems Engineering
Mind map on the success and failure of using fanless PCs
Success of fanless PCs thank to robustness, reliability, maintenance-free, energy efficiency, etc.
